How It Works
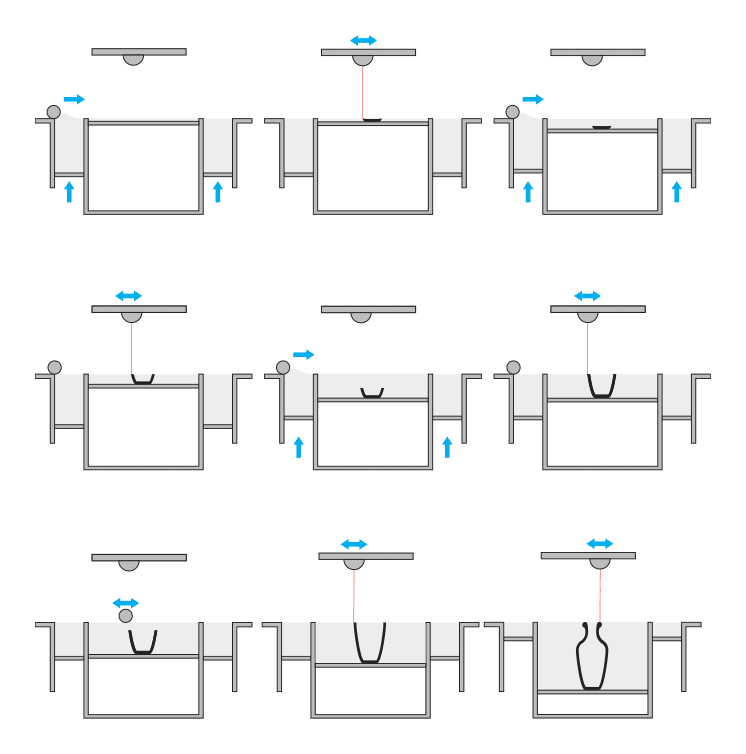 Section view of the printing process
Section view of the printing process
Metal 3D Printing is a laser-based technology that uses powdered metals. Similar to Laser Sintering, a high-powered laser selectively binds together particles on the powder bed while the machine distributes even layers of metallic powder. Support structures are automatically generated and built simultaneously in the same material and are later manually removed. Once complete, the part undergoes heat treatment.
Materials
Aluminum
- A light and strong metal
- Mainly used for spare parts and full functional models
Titanium
- The strongest material we currently 3D print in
- Jewelry safe and biocompatible
- Mainly used for jewelry, spare parts and full functional models
Trivia
Did you know that?
- Direct Metal Laser sintering has its roots in the 1970s. In 1971, Frenchman Pierre Ciraud filed a patent application describing a method for manufacturing objects of any geometry by applying powdered material onto a substrate and solidifying it by means of a beam of energy.
- The first test system for Direct Metal Laser Sintering was installed already in 1994 while the first commercial EOSINT M 250 systems were installed in the summer of 1995.








